Multi-chassis LAG (MC-LAG) is an extension
to the LAG feature to provide not only link redundancy but also node-level
redundancy. This feature is not defined in any IEEE standard, but Alcatel-Lucent
has developed a proprietary solution.
to the LAG feature to provide not only link redundancy but also node-level
redundancy. This feature is not defined in any IEEE standard, but Alcatel-Lucent
has developed a proprietary solution.
A proprietary messaging between
redundant-pair nodes supports coordinating the LAG
switchover.
redundant-pair nodes supports coordinating the LAG
switchover.
Multi-chassis LAG supports LAG switchover
coordination: one node connected to two redundant-pair peer nodes with the LAG.
During the LACP negotiation, the redundant-pair peer nodes act like a single
node using active/stand-by signaling to ensure that only links of one peer nodes
is used at a time.
coordination: one node connected to two redundant-pair peer nodes with the LAG.
During the LACP negotiation, the redundant-pair peer nodes act like a single
node using active/stand-by signaling to ensure that only links of one peer nodes
is used at a time.
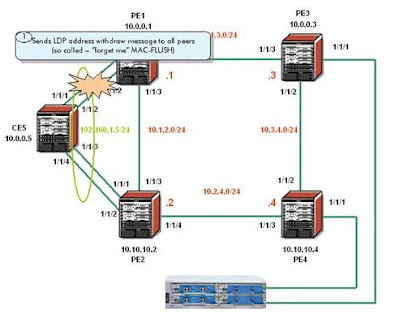
In this Configuration Note a setup is built
with 1 CE and 4 PEs. The CE node can be any routing/switching device that can be
configured for LACP. The PE routers can be SR, SRc or ESS. Figure 1
shows the physical topology of the setup:
with 1 CE and 4 PEs. The CE node can be any routing/switching device that can be
configured for LACP. The PE routers can be SR, SRc or ESS. Figure 1
shows the physical topology of the setup:
Note the test tool Figure 1 is only used to
send/receive traffic to create MAC entries in the VPLS service. It can be
replaced by a router/switch.
send/receive traffic to create MAC entries in the VPLS service. It can be
replaced by a router/switch.
Configuration
Base
Topology
This Configuration Note assumes that
following base configuration has been implemented on the PEs:
following base configuration has been implemented on the PEs:
-
Cards, MDAs and ports configured
-
Interfaces configured
-
IGP configured and converged
-
MPLS configured
-
SDPs configured between all PE
routers
Note
that you can choose between OSPF and ISIS as the IGP. Both LDP or RSVP
can be used for signaling the transport MPLS labels. Alternatively, GRE
can be used for the transport tunnels.
It
does not matter if the SDPs are using LDP, RSVP or GRE. RSVP has the
added value of offering FRR to get faster convergence in the core.
In this setup OSPF and LDP are used.
The following commands can be used to check if OSPF has converged and to make sure the SDPs are up:
*A:PE1# show router route-table
==============================
Route Table (Router: Base)
==============================
Dest Prefix
Next Hop[Interface Name]
------------------------------
10.0.0.1/32
system
10.0.0.2/32 Remote OSPF 00h27m17s 10
10.1.2.2
10.0.0.3/32
10.1.3.3
10.0.0.4/32
10.1.2.2
10.1.2.0/24
toPE2
10.1.3.0/24
toPE3
10.2.4.0/24
10.1.2.2
10.3.4.0/24
10.1.3.3
------------------------------
No. of Routes: 8
==============================
*A:PE1# show service sdp
==============================
Services: Service Destination Points
==============================
SdpId Adm MTU Opr MTU IP address Adm Opr Deliver Signal
------------------------------
12 0 9190 10.0.0.2 Up Up LDP TLDP
13 0 9190 10.0.0.3 Up Up LDP TLDP
14 0 9190 10.0.0.4 Up Up LDP TLDP
------------------------------
Number of SDPs : 3
MC-LAG Configuration
LAG configuration on CEs
Auto-negotiation needs to be switched off (or configured to limited) on all ports that will be included into the LAG.
Configure LACP on the LAG. At least 1 side of the LAG needs to be configured in ‘active’ mode.
*A:CE5# configure port 1/1/[1..4] ethernet no autonegotiate
*A:CE5# configure port 1/1/[1..4] no shut
*A:CE5# configure lag 1 port 1/1/1 1/1/2 1/1/3 1/1/4
*A:CE5# configure lag 1 lacp active
*A:CE5# configure lag 1 no shutdown
LAG configuration on PEs
The
PE ports facing the CEs have to be configured as access ports since
they will be used in the VPLS service. The LAG also needs to be
configured in mode access.
Remark: the LAG encapsulation type (null|dot1q|qinq) must match the port encapsulation type of the LAG members.
Auto-negotiation needs to be switched off (or configured to limited).
Configure LACP on the LAG. At least 1 side of the LAG needs to be configured in ‘active’ mode.
*A:PE1# configure port 1/1/[1..2] ethernet no autonegotiate
*A:PE1# configure port 1/1/[1..2] ethernet mode access
*A:PE1# configure port 1/1/[1..2] no shut
*A:PE1# configure lag 1 mode access
*A:PE1# configure lag 1 port 1/1/1 1/1/2
*A:PE1# configure lag 1 lacp active
*A:PE1# configure lag 1 no shutdown
MC-LAG configuration on PE1 and PE2
The redundant PEs must act as 1 virtual node toward the CE. They have to communicate the same LACP parameters to the CE side.
3 parameters uniquely identify a LAG instance:
-
lacp-key
-
system-id
-
system-priority
These 3 parameters must be configured with the same value on both redundant PEs.
Configure multi-chassis redundancy with a peering session toward the redundant PE system address and enable mc-lag redundancy.
*A:PE1# configure redundancy multi-chassis
*A:PE1>config>redundancy>
------------------------------
peer 10.0.0.2 create
mc-lag
lag 1 lacp-key 1 system-id 00:00:00:00:00:01 system-priority 100
no shutdown
exit
no shutdown
exit
------------------------------
*A:PE2# configure redundancy multi-chassis
*A:PE2>config>redundancy>
------------------------------
peer 10.0.0.1 create
mc-lag
lag 1 lacp-key 1 system-id 00:00:00:00:00:01 system-priority 100
no shutdown
exit
no shutdown
exit
------------------------------
MC-LAG Verification
Verify MC peers
*A:PE1# show redundancy multi-chassis sync
==============================
Multi-chassis Peer Table
==============================
Peer
------------------------------
Peer IP Address : 10.0.0.2
Authentication : Disabled
Source IP Address : 0.0.0.0
Admin State : Enabled
==============================
==============================
Note
that if the source IP address is not configured explicitly the output
shows ‘0.0.0.0’. In that case the system IP address will be used as
source. (In future releases ‘0.0.0.0’ will be replaced by the used Source IP Address)
The source IP address can be configured with the command:
*A:PE1# configure redundancy multi-chassis
*A:PE1>config>redundancy>
Authentication can also be configured:
*A:PE2# configure redundancy multi-chassis
*A:PE2>config>redundancy>
Remark: when configuring authentication or a source address the MC peer needs to be shutdown first.
If source IP address and authentication are configured the result looks like:
*A:PE1# show redundancy multi-chassis sync
==============================
Multi-chassis Peer Table
==============================
Peer
------------------------------
Peer IP Address : 10.0.0.2
Authentication : Enabled
Source IP Address : 10.0.0.1
Admin State : Enabled
==============================
==============================
Verify MC-LAG peer status and LAG parameters
*A:PE1# show redundancy multi-chassis mc-lag peer 10.0.0.2
==============================
Multi-Chassis MC-Lag Peer 10.0.0.2
==============================
Last Changed : 03/07/2007 17:38:53
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
KeepAlive : 10 deci-seconds Hold On Ngbr Failure : 3
------------------------------
Lag Id Lacp Key Remote Lag Id System Id Sys Prio Last Changed
------------------------------
1 1 1 00:00:00:00:00:01 100 03/07/2007 17:40:17
------------------------------
Number of LAGs : 1
==============================
In
this example the Lag-Id is 1 on both redundant PEs. This is not
mandatory. If the Lag-Id on PE2 is eg. 2, the following should be
configured on PE1:
*A:PE1# configure redundancy multi-chassis
*A:PE1>config>redundancy>
Verify MC-LAG status
*A:PE1# show lag 1
==============================
Lag Data
==============================
Lag-id Adm Opr Port-Threshold Up-Link-Count MC Act/Stdby
------------------------------
1 up down 0 0 standby
==============================
*A:PE2# show lag 1
==============================
Lag Data
==============================
Lag-id Adm Opr Port-Threshold Up-Link-Count MC Act/Stdby
------------------------------
1 up up 0 2 active
==============================
In this case the Lag on PE2 is Active/Operationally up whereas the Lag on PE1 is Standby/Operationally down.
The
selection criteria by default is highest # of links and priority. In
this example the # of links and the priority of the links is the same on
both redundant PEs. Whichever PE’s LAG gets in operational up status
first will be the active.
LAG
ports of one PE could be preferred over the other PE by configuring
port priority (e.g. the following command lowers the priority of the LAG
ports on PE1, thus giving this LAG higher preference).
*A:PE1# configure lag 1 port 1/1/1 1/1/2 priority 10
Note : lower S priority is preferred
Verify detailed MC-LAG status on PE1
*A:PE1# show lag 1 detail
==============================
LAG Details
==============================
Description:
------------------------------
Details
------------------------------
Lag-id : 1 Mode : access
Adm : up Opr : up
Thres. Exceeded Cnt : 19 Port Threshold : 0
Thres. Last Cleared : 03/07/2007 19:57:18 Threshold Action : down
Dynamic Cost : false Encap Type : null
Configured Address : 1e:2f:ff:00:01:41 Lag-IfIndex : 1342177281
Hardware Address : 1e:2f:ff:00:01:41 Adapt Qos : distribute
Hold-time Down : 0.0 sec
LACP : enabled Mode : active
LACP Transmit Intvl : fast LACP xmit stdby : enabled
Selection Criteria : highest-count Slave-to-partner : disabled
Number of sub-groups: 1 Forced : -
System Id : 1e:2f:ff:00:00:00 System Priority : 32768
Admin Key : 32768 Oper Key : 1
Prtr System Id : 1e:2d:ff:00:00:00 Prtr System Priority : 32768
Prtr Oper Key : 32768
MC Peer Address : 10.0.0.2 MC Peer Lag-id : 1
MC System Id : 00:00:00:00:00:01 MC System Priority : 100
MC Admin Key : 1 MC Active/Standby : active
MC Lacp ID in use : true MC extended timeout : false
MC Selection Logic : peer decided
MC Config Mismatch : no mismatch
------------------------------
Port-id Adm Act/Stdby Opr Primary Sub-group Forced Prio
------------------------------
1/1/1 up active up yes 1 - 10
1/1/2 up active up 1 - 10
------------------------------
Port-id Role Exp Def Dist Col Syn Aggr Timeout Activity
------------------------------
1/1/1 actor No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
1/1/1 partner No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
1/1/2 actor No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
1/1/2 partner No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
==============================
After changing the Lag port priorities the Lag on PE1 is in up/up state and the ports are in up/active/up status.
This
show command also displays MC peer info and actor info. More
information about this can be found in the MC-LAG workshop presentation.
VPLS Configuration
Configure
a VPLS service on every PE and add SAPs and SDPs. In this example
mesh-SDPs are used. In case of a BTV service spoke-SDPs in combination
with R/MSTP can be used to avoid sending duplicate traffic.
*A:PE1>config>service>vpls# info
------------------------------
stp
shutdown
exit
sap lag-1 create
exit
mesh-sdp 12:60 create
exit
mesh-sdp 13:60 create
exit
mesh-sdp 14:60 create
exit
no shutdown
------------------------------
Likewise, a VPLS service, SAPs and mesh-SDPs need to be configured on the other PE routers.
VPLS Service Verification
Verify service status
*A:PE1# show service service-using
==============================
Services
==============================
ServiceId Type Adm Opr CustomerId Last Mgmt Change
------------------------------
60 VPLS Up Up 1 03/09/2007 20:32:34
------------------------------
Matching Services : 1
------------------------------
==============================
The VPLS service should be Up on all PE routers.
Verify FDB of the VPLS service.
On CE5 and on the 2 ports of the tester create ip interfaces in the same subnet.
Note that you could also create an Epipe service and connect the test tool to it.
*A:CE5>config>router>if# info
------------------------------
address 192.168.1.5/24
port lag-1
------------------------------
Send
traffic from CE5 towards the ports of the test tool. E.g. ping the
access port connected on PE3. You can check the FDB on PE3:
*A:PE3# show service id 60 fdb detail
==============================
Forwarding Database, Service 60
==============================
ServId MAC Source-Identifier Type/Age Last Change
------------------------------
60 1e:2e:ff:00:01:41 sdp:31:60 L/0 03/12/2007 17:48:20
60 1e:4e:01:01:00:01 sap:1/1/1 L/0 03/12/2007 17:48:20
------------------------------
No. of MAC Entries: 2
==============================
Notice
that the first entry shows MAC address of the LAG configured on CE5.
The MAC address was learned via sdp:31:60. Stop sending traffic.
*A:CE5# show lag detail
==============================
LAG Details
==============================
------------------------------
LAG 1
------------------------------
Description:
------------------------------
Details
------------------------------
Lag-id : 1 Mode : network
Adm : up Opr : up
Thres. Exceeded Cnt : 36 Port Threshold : 0
Thres. Last Cleared : 03/04/2002 16:31:13 Threshold Action : down
Dynamic Cost : false Encap Type : null
Configured Address : 1e:2e:ff:00:01:41 Lag-IfIndex : 1342177281
Hardware Address : 1e:2e:ff:00:01:41
...
In Figure 3
the active access link between CE5 and PE1 is broken (e.g. by shutting
down port 1/1/1 on PE1). The MC-Lag will switch to PE2 and PE1 will send
out an LDP MAC-Flush message over all mesh-SDPs.
*A:PE3# show service id 60 fdb detail
==============================
Forwarding Database, Service 60
==============================
ServId MAC Source-Identifier Type/Age Last Change
------------------------------
60 1e:4e:01:01:00:01 sap:1/1/1 L/15 03/12/2007 17:48:20
------------------------------
No. of MAC Entries: 1
==============================
Note that the MAC address was flushed from the FDB on PE3.
If the same test is done but 1/1/1 is shut on CE5 instead of PE1 the result is different:
*A:PE3# show service id 60 fdb detail
==============================
Forwarding Database, Service 60
==============================
ServId MAC Source-Identifier Type/Age Last Change
------------------------------
60 1e:2e:ff:00:01:41 sdp:32:60 L/0 03/12/2007 17:48:39
60 1e:4e:01:01:00:01 sap:1/1/1 L/15 03/12/2007 17:48:20
------------------------------
No. of MAC Entries: 2
(source: http://networkaids.blogspot.com/2010/01/multi-chassis-lag-mc-lag-in-vpls.html)


Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét